© 2025 Healix Health. All rights Reserved || Developed by Batechnology.org
Sexual Health Service
Sexual health services play a crucial role in promoting overall well-being and preventing a wide range of health issues. These services encompass a broad spectrum of care, from education and prevention to diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), family planning, and support for sexual dysfunction. Here, we will explore the importance, components, and accessibility of sexual health services.
Importance of Sexual Health Services
Sexual health is a fundamental aspect of an individual’s overall health and quality of life. Proper sexual health services can:
- Prevent STIs and Unplanned Pregnancies: Regular screenings, vaccinations (like the HPV vaccine), and contraceptive counseling help prevent the spread of STIs and reduce the incidence of unplanned pregnancies.
- Promote Healthy Relationships: Education on consent, healthy relationships, and sexual rights fosters respectful and consensual sexual interactions.
- Support Mental Health: Addressing sexual health concerns can alleviate stress, anxiety, and depression associated with sexual dysfunctions or STIs.
- Enhance Quality of Life: Access to comprehensive sexual health services empowers individuals to make informed choices about their sexual health, leading to improved overall well-being.
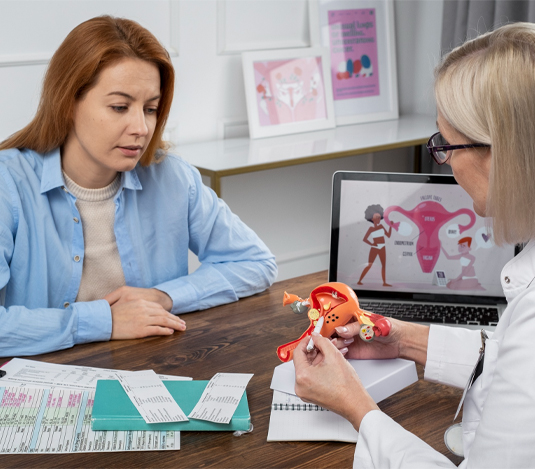
Components of Sexual Health Services
Sexual health services typically include:
Education and Counseling:
- Comprehensive sex education covering anatomy, contraception, STI prevention, consent, and healthy relationships.
- Counseling for individuals and couples on sexual health issues, relationship concerns, and sexual orientation or gender identity.
Screening and Testing:
- Regular STI screenings and HIV testing, crucial for early detection and treatment.
- Pap smears and HPV testing for cervical cancer prevention.
Vaccinations:
- HPV vaccine to prevent cervical and other cancers caused by human papillomavirus.
- Hepatitis B vaccine to prevent liver infection and disease.
Contraceptive Services:
- A variety of contraceptive options, including pills, intrauterine devices (IUDs), implants, condoms, and emergency contraception.
- Counseling on choosing the most appropriate method based on individual needs and preferences.
Treatment and Management:
- Treatment for STIs, including medication and follow-up care.
- Management of sexual dysfunctions, such as erectile dysfunction, low libido, or painful intercourse.
Support Services:
- Support for survivors of sexual assault, including medical care, counseling, and legal assistance.
- Resources for LGBTQ+ individuals, including hormone therapy, mental health support, and HIV prevention.
Accessibility and Barriers
Access to sexual health services varies widely depending on geographic location, socioeconomic status, and cultural factors. Key barriers include:
Stigma and Discrimination:
- Stigma surrounding STIs, sexual orientation, and gender identity can prevent individuals from seeking care.
- Discrimination within healthcare settings can lead to inadequate care or deter individuals from accessing services.
Lack of Education:
- Limited sex education in schools and communities can result in a lack of awareness about available services and their importance.
Financial Barriers:
- Cost of services and lack of insurance coverage can make sexual health care inaccessible to many individuals.
Geographic Barriers:
- Rural and remote areas often lack adequate sexual health services, requiring individuals to travel long distances for care.
